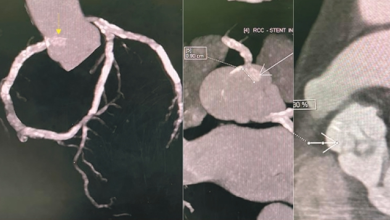
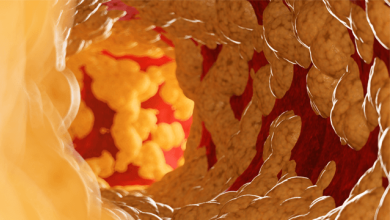
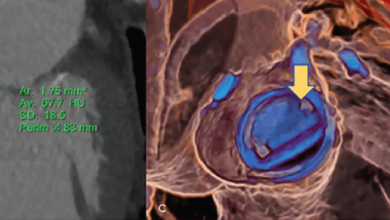
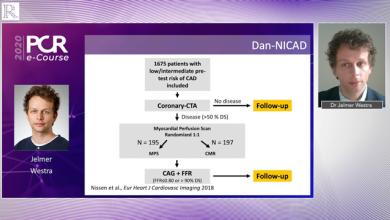
Over the last decade, cardiac CT technology has experienced revolutionary changes and gained broad clinical acceptance in the work-up of patients with coronary artery disease (CAD). Since cardiac multidetector-row CT (MDCT) was introduced in 1998, acquisition time, number of detector rows and spatial and temporal resolution have improved tremendously.
Current developments in cardiac CT are focusing on low-dose cardiac scanning at ultra-high temporal resolution. Technically, there are two major approaches to achieving these goals: rapid data acquisition using dual-source CT scanners with high temporal resolution or volumetric data acquisition with 256/320-slice CT scanners. While each approach has specific advantages and disadvantages, both technologies foster the extension of cardiac MDCT beyond morphological imaging towards the functional assessment of CAD.
MRI techniques offer a high soft-tissue contrast-to-noise ratio in comparison with that seen with X-ray, CT and ultrasound. Interventional MRI is a growing field, and the strength of MRI guidance for procedures rests fundamentally in the high-contrast imaging of soft tissue structures. Combined with the avoidance of radiation exposure, the potential for functional assessment and the ability to exploit MR signals for calculation of the location of interventional instruments, it is clear that the implementation of interventional MRI will continue to grow.